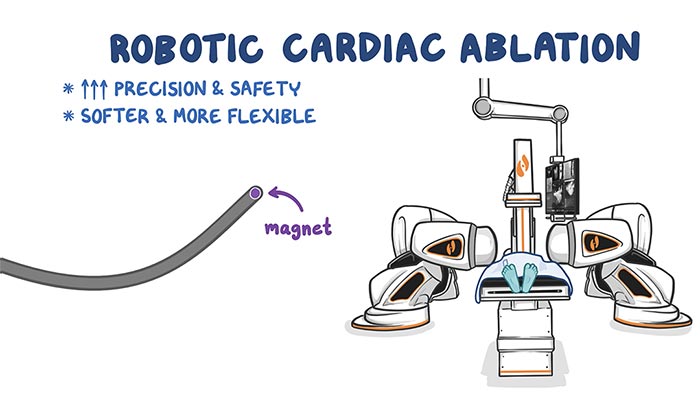
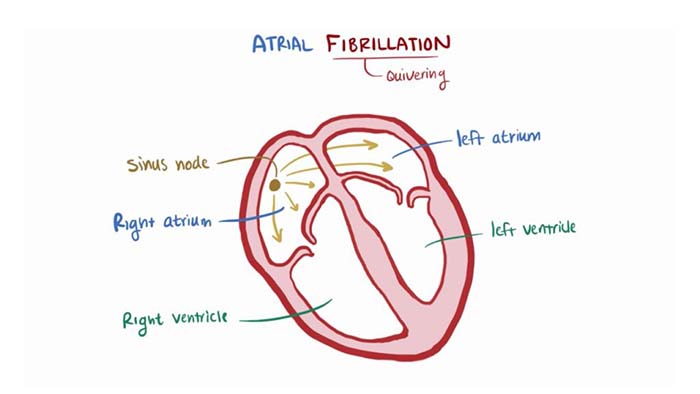
In traditional cardiac ablation procedures, a physician manually manipulates a catheter by hand to treat the heart. Controlling a catheter tip by holding onto the opposite end isn’t easy. The challenge could be compared to writing your name while holding a pencil by its eraser.
References & Intended Uses
- Data on file
- Link to study
- The hospital locator directory provides contact information for hospitals that treat cardiac arrhythmias using Stereotaxis’ Niobe RMN system. Stereotaxis does not charge any healthcare provider to be included in this directory, nor does Stereotaxis verify the accuracy of any information provided by physicians included in this hospital locator directory. Stereotaxis does not endorse or recommend any individual physician, practice or healthcare facility. Ask your healthcare provider what is right for you. Only a licensed healthcare provider should diagnose cardiac arrhythmias and recommend treatment options.
Stereotaxis Intended Use Statements, United States Labeling:
The Genesis RMN® and Niobe® ES Systems are intended to navigate compatible magnetic devices through tissue to designated target sites in the right and left heart, coronary vasculature, neurovasculature, and peripheral vasculature by orienting the device tip in a desired direction. The Cardiodrive® Catheter Advancement System (CAS) is intended to automatically advance and retract compatible magnetic electrophysiology (EP) mapping and ablation catheters inside a patient’s heart when used in conjunction with a Stereotaxis magnetic navigation system. The Cardiodrive System is not intended to advance the EP mapping and ablation catheters through the coronary vasculature or the coronary sinus.
Consult the associated product labeling for the Indications for Use and instructions of other devices used in conjunction with Stereotaxis products.
Cardiodrive and Niobe are trademarks of Stereotaxis, Inc., registered in the United States, the European Community, and Japan. Genesis RMN is a trademark of Stereotaxis, Inc., registered in the United States.